Data governance frameworks are structured approaches to managing and using data in an organization. They include policies, procedures and standards that guide how data is collected, stored, managed and used. These frameworks help with data quality, data integration, data privacy and security, and effective data architecture.
Organizations collect and store more data than ever before. This data can be used to improve business processes, but it can also be a risk if handled poorly. Data governance frameworks have therefore become an invaluable way to protect your customers' privacy and comply with the latest privacy laws. However, organizations must implement a data governance framework that goes beyond basic data quality and management.
SEE: Take advantage of this database engineer hiring kit from TechRepublic Premium.
To govern data effectively, organizations must have a clear understanding of their data landscape. They need to know where their data comes from, who owns it, how it is used and where it is stored. Gathering this information to build a data governance framework requires close collaboration between different departments and business units.
How data governance frameworks work
Data governance is not just about complying with the law or managing risk, but about effectively harnessing the power of data to drive decision-making, innovation and competitive advantage.
The primary goal of implementing a data governance framework is to create a systematic approach to managing data throughout its entire lifecycle. This means establishing internal standards and policies, defining ownership and management, and formulating processes for quality, security, compliance, and privacy management. The ultimate goal is to create an internal culture where data is treated as a critical business asset.
Examples of data governance frameworks
Below is a list of some commonly referenced data governance frameworks:
Each of these frameworks has its own pros and cons. Organizations should select the data governance framework that best aligns with their unique needs and objectives.
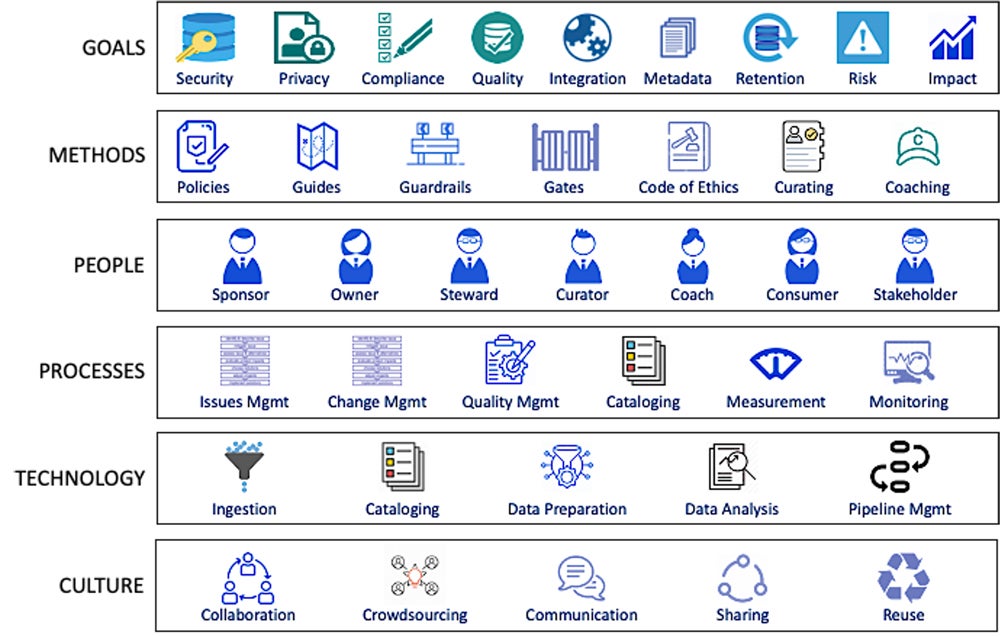
Types of data governance frameworks
There are two opposing philosophies for creating data governance frameworks that offer different pros and cons depending on an organization's specific goals.
Bottom-up philosophy
The bottom-up approach to data governance, popularized by the growing big data movement, starts with raw data. Data is first ingested and then structures or schemas are built on top of the data once it has been read. Governance rules, policies, and quality controls are also added to the data set at this time.
The advantage of this approach is its scalability. However, it can be difficult to maintain consistent quality control over a large volume of data.
Top down philosophy
In the top-down approach, data modeling and governance take priority and are the first steps in developing a data governance framework. The process begins with data professionals applying well-defined methodologies and best practices to data. The advantage of this approach is its focus on quality control.
Components of a data governance framework
There are four main components of a data governance framework:
- Data management: Data stewards ensure that an organization's data assets are accurate, consistent, and comply with all relevant regulations, especially in the course of company projects.
- Data quality management: Data quality management includes processes and procedures used to ensure that an organization's data assets are free from errors and inaccuracies, as well as methods to identify and correct any errors or inaccuracies.
- Data management: Data management processes define how an organization's data assets are created, stored, accessed, and used, and establish the rules for how those assets will be shared with internal and external stakeholders.
- Technology infrastructure: This refers to the hardware and software systems used to collect, store and manage data. These include databases, enterprise resource planning systems, data warehouses, and network connections that facilitate the exchange of information between interested parties.
Pillars of data governance frameworks
Data governance frameworks are based on four key pillars that ensure the effective management and use of data across the organization. These pillars ensure that data is accurate, can be effectively combined from different sources, is protected and used in accordance with laws and regulations, and is stored and managed in a way that meets the needs of the organization.
1. Data quality
Data quality is the cornerstone of any data governance framework. Ensures that data used in decision-making processes is accurate, consistent and reliable. Additionally, data quality management involves establishing policies and procedures for data validation, cleaning, and profiling.
SEE: Explore these superior data quality tools and software.
2. Data integration
Data integration involves combining data from different sources using various tools to provide a unified view. This pillar ensures that data from multiple departments, business units, or external partners can be merged and used effectively for analysis and decision making.
3. Privacy and data security
Data privacy and security are crucial in today's digital age. This pillar involves implementing policies and procedures to protect sensitive data and comply with data protection laws and regulations. It includes data encryption, access control and data anonymization techniques.
4. Data architecture
The fourth pillar is data architecture, which refers to the design and structure of data systems. It involves planning and designing data systems to ensure they meet the needs of the organization. This includes the design of databases, data warehouses, and data lakes.
Why is a data governance framework necessary?
We can identify three main reasons:
- Maintain a standard set of policies and procedures: Without such a framework, critical data assets risk becoming fragmented, inaccurate, and non-compliant with relevant regulations.
- Avoid rudderless effort: Lack of governance can lead to confusion and duplication of effort as different departments or individual users try to manage data with their own methods.
- Normative compliance: A data governance framework ensures compliance with various laws and regulations, from HIPAA to GDPR.
Best practices for creating a data governance framework
The first step in creating an effective data governance framework begins with a clear understanding of the organization's objectives and the role that proper data management plays in achieving them.
It is also advisable to focus on simplicity and flexibility when developing a data governance framework. Too many unnecessary rules can hinder adoption, while flexibility (without compromising security and compliance) ensures quick adaptation to a changing business or regulatory environment.
Engage stakeholders in an ongoing dialogue to refine data governance practices when they become obsolete. Finally, you should invest in the right data governance tools to optimize your operations.
SEE: For more detailed information, see our guide on data governance best practices.









